Business Foundation
BUSINESS DECISION MAKING - A1
Business Case Study
Table of Contents
expand_more expand_lessDETAILED INSTRUCTION
I. ASSESSMENT RECAP
Word Limit: 800 words excluding tables, figures, and references.
Overview:
- The task involves applying concepts learned in the first four weeks, focusing on cost behavior, Cost-Volume-Profit analysis, budget preparation, and analysis.
- Students are required to create a budgeting plan for a business type assigned based on the last two digits of their student ID.
- The business types include fashion shops, coffee shops, restaurants, and supermarkets.
- The budget plan should cover from quarter 3 of 2023 to quarter 2 of 2024, including sales, cost, profit, and cash budgets.
Criteria:
- The assignment consists of several questions, each carrying specific marks, totaling 20 marks.
- Students are expected to demonstrate their understanding of strategic, tactical, and operational decisions, distinguish between fixed and variable costs, and analyze market changes affecting business costs.
- The assignment includes budget planning, contribution margin calculation, operating profit before and after tax, net cash flow, and a decision on equipment purchase.
- Students also need to analyze the budget plan, prepare a SWOT analysis, and make a decision regarding business expansion.
II. WORD EXPLANATION
Strategic Decisions: These are long-term choices made by the top management of a company, which fundamentally impact the company's direction. They often involve large-scale investment and affect the overall growth and sustainability of the business.
Tactical Decisions: These decisions are medium-term and are generally taken by middle-level management. They are focused on the implementation of strategies set by top management and often involve how resources are allocated and managed.
Operational Decisions: These are short-term decisions, usually made on a day-to-day basis. They are focused on the operations of the company, such as scheduling, inventory management, and maintenance.
Fixed Costs: These are expenses that do not change with the level of goods or services produced by the business. Examples include rent, salaries, and insurance.
Variable Costs: Costs that vary depending on the level of production or service delivery. These include costs for raw materials, utility expenses that vary with usage, and commission-based wages.
Inflation: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and, subsequently, the purchasing power of currency is falling.
Contribution Margin: This is the selling price per unit, minus the variable cost per unit. It represents the portion of sales revenue that is not consumed by variable costs and contributes to covering fixed costs.
Operating Profit: This is the profit earned from a firm's normal core business operations. It excludes deductions for interest and taxes.
Net Cash Flow: The amount of cash generated or lost over a specific period. This is calculated by taking the sum of cash inflows and outflows from various business activities.
SWOT Analysis: A strategic planning technique used to identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition or project planning.
Revenue Growth: The increase in a company's sales over a period. It's an indicator of how fast a company is expanding.
III. DETAILED OUTLINE
Question 1: Business Introduction
- First, you should introduce the business in a way that readers can understand your specific business. For example, name, size, products,...
Hints:
- Specify the nature of the business. Is it a retail establishment, a service-oriented business, a manufacturing entity, a dining venue, or a café?
- Elaborate on the scale of the business. Is it a quaint local store, a business of moderate size, or something else?
- Identify the intended customer base or market segment. Who forms the core clientele of this business?
Example: Type of business “Coffee shop"
The Tiny Post Cafe is a cozy, family-owned coffee shop known for its unique and artisanal coffee blends, as well as a variety of homemade pastries and snacks, all offered at reasonable prices. The coffee shop boasts a warm and inviting atmosphere, creating a sense of community among its patrons. Although it has a somewhat limited seating area, it's a popular spot for locals, students, and remote workers, particularly appreciated for its quiet ambiance and free Wi-Fi. It's especially frequented by regulars during early mornings and weekends, making it a cherished part of the neighborhood.
- You should examine the business model and identify key areas for strategic, tactical, and operational decisions.
+ Strategic: Focus on long-term goals and business growth.
+ Tactical: Look at medium-term actions that support strategic decisions.
+ Operational: Consider day-to-day operational choices and efficiencies.
Example: Type of business “Coffee Shop"
|
Strategic |
Brand development and expansion. Hace new menu items. |
|
Tactical |
Recruit skilled bartenders. Marketing Campaigns and Vouchers. |
|
Operational |
Inventory management. Staff scheduling. |
Question 1
Suggested flow:
- The business name and the kind of products it offers.
- The total branches and annual revenue, indicating the business's size.
- Strategic decisions of the business, like the value proposition and target customer segments.
- Tactical decisions tailored to fulfill the established strategy.
- Operational choices corresponding to each strategic plan.
Example:
BiMelted, a medium-sized establishment in Hanoi, specializes in sandwiches and coffee. With a single location, its annual revenue is around $200,000.
Strategically, BiMelted focuses on offering delectable, convenient meals that resonate with local tastes. To realize this, the restaurant employs tactics like social media marketing and diverse advertising campaigns to enhance brand recognition and draw in new patrons. Operationally, BiMelted prioritizes recipe innovation, adjusting its sandwich offerings to incorporate seasonal ingredients. Additionally, it concentrates on maintaining high customer satisfaction, strategically choosing delivery partners, and selecting seasonally and locally available raw materials.
Question 2:
Requirement:
● Identify short lists of ‘fixed’ costs and ‘variable’ costs from the specific business
● Explain why you believe they are variable costs or fixed costs.
● Explain why it is important for you to be able to recognise the difference between fixed costs and variable costs.
Hints:
- Guideline: suggest 150 words
- List the costs in the excel sheet
- Distinguish between 2 types of costs based on:
● The business' fixed cost is the fees that the restaurant is obligated to pay and remain unchanged regardless of sales. Examples include rent for the restaurant space, salaries of permanent staff, and insurance premiums.
● Variable costs change depending on sales revenue. As sales increase or decrease, these costs adjust accordingly. They include costs of ingredients, utilities (to some extent, as more customers mean more usage of utilities), and packaging for takeaways or deliveries.
- Emphasizes the purpose of distinguishing between fixed and variable costs:
● Clarify the business's current behavior cost
● Determine whether the current selling price makes a profit
● Estimate break-even point to build reasonable sales goals
Example:
For BiMelted, a sandwich and coffee restaurant in Hanoi, the monthly fixed costs include:
Rent: $1,000 for a 70m² location on Hoang Dieu Street, close to the city center. This cost is a standard expense regardless of the restaurant's sales volume.
Employee Salaries: $450 for each of the four employees, totaling $1,800. These salaries are constant each month, independent of the restaurant's revenue.
Advertisement Fees: $100 for marketing on various social media platforms. This is a set amount allocated monthly for digital marketing efforts.
These fixed costs are obligatory and do not fluctuate with sales. In contrast, variable costs are influenced by sales and production levels. These include the cost of raw ingredients and packaging materials, which vary according to the quantity of food and beverages sold. The more items BiMelted sells, the higher these costs will be.
It is fundamental to differentiate fixed costs from variable costs so that the business can understand its cost behavior, and cost oscillations as output changes to determine a profitable but competitive selling price for the product. Besides, identifying each type of cost also helps businesses easily estimate the break-even point to set a reasonable and attainable target.
Example: Type of business “Coffee shop"
|
Fixed Cost |
Rent. Insurance. Salaries of permanent staff. |
|
Variable Cost |
Coffee beans, milk, sugar, pastries,.. Utilities (electricity and water) |
Question 3: External Factors
- You should research economic indicators like inflation rates. Use graphs to help readers easily visualize how external factors would impact the business.
Example: Vietnam’s inflation rate from 1987 to 2028
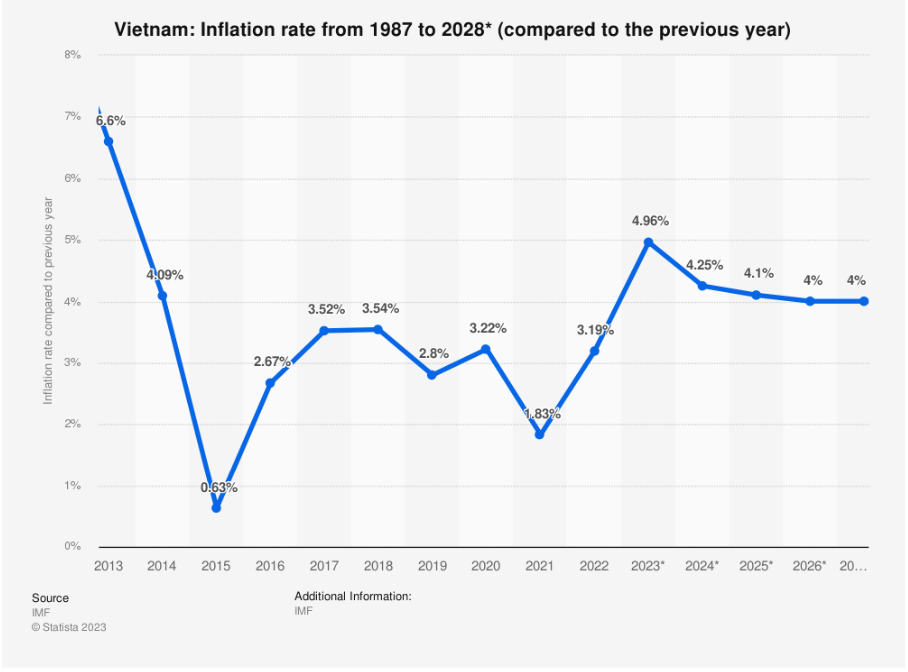
In 2023, Vietnam witnessed a 4.96% inflation rate, projected to increase further. This inflationary trend poses challenges for coffee shops
Charge your account to get a detailed instruction for the assignment