Econ fin
MACRO FOR DECISION MAKING - A3
Nation Report
Table of Contents
expand_more expand_lessDETAILED INSTRUCTION
A/ ASSIGNMENT RECAP
The assignment involves three main sections:
● First, it requires an analysis of 2-3 significant macroeconomic events in the Vietnamese economy over the past year and their impacts on various sectors and the well-being of residents.
● The second section involves presenting economic data and using the IS-LM framework to assess government policy impacts, as well as discussing industries with growth rate changes.
● In the final section, students need to provide 3 to 5 well-considered policy recommendations based on the findings from the first two sections, focusing on both short-term support and long-term prosperity, as well as industries discussed in the second section.
Suggested Structure:
I. Section 1: Events
A. Introduction
B. & C. Event/Condition 1&2
D. Conclusion
II. Section 2: Economic Activity
A. Data Presentation
B. IS-LM Framework
C. Industry Analysis
III. Section 3: Recommendation
Suggestion
● Ongoing impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic - Disruptions to tourism, manufacturing, services. Increased unemployment, lower incomes.
● Rising inflation and currency devaluation - Rising prices reduce household purchasing power. Currency issues complicate trade.
● Natural disasters/climate events - Floods, droughts disrupt agriculture, infrastructure. Environmental impacts also emerge.
● Changing global energy dynamics - Vietnam's economy relies on oil and coal exports, so shifts in demand and prices have wide impacts.
● Supply chain issues - Disruptions to manufacturing and exports due to shortages and delays of imported inputs.
● Trade policy shifts by major partners - Vietnam's trade outlook shaped by dynamics with US, China, EU, ASEAN. Policy changes influence exports.
● Technology/automation advancement - Can disrupt industries and employment if skills don't keep pace. But also productivity benefits.
● Ukraine-Russia War - Disruptions to food and energy exports. Rise in commodity prices. Increased uncertainty weighing on Vietnamese manufacturing, trade, and investment. Geopolitical impacts on economic relations.
B/ KEYWORD EXPLANATIONS
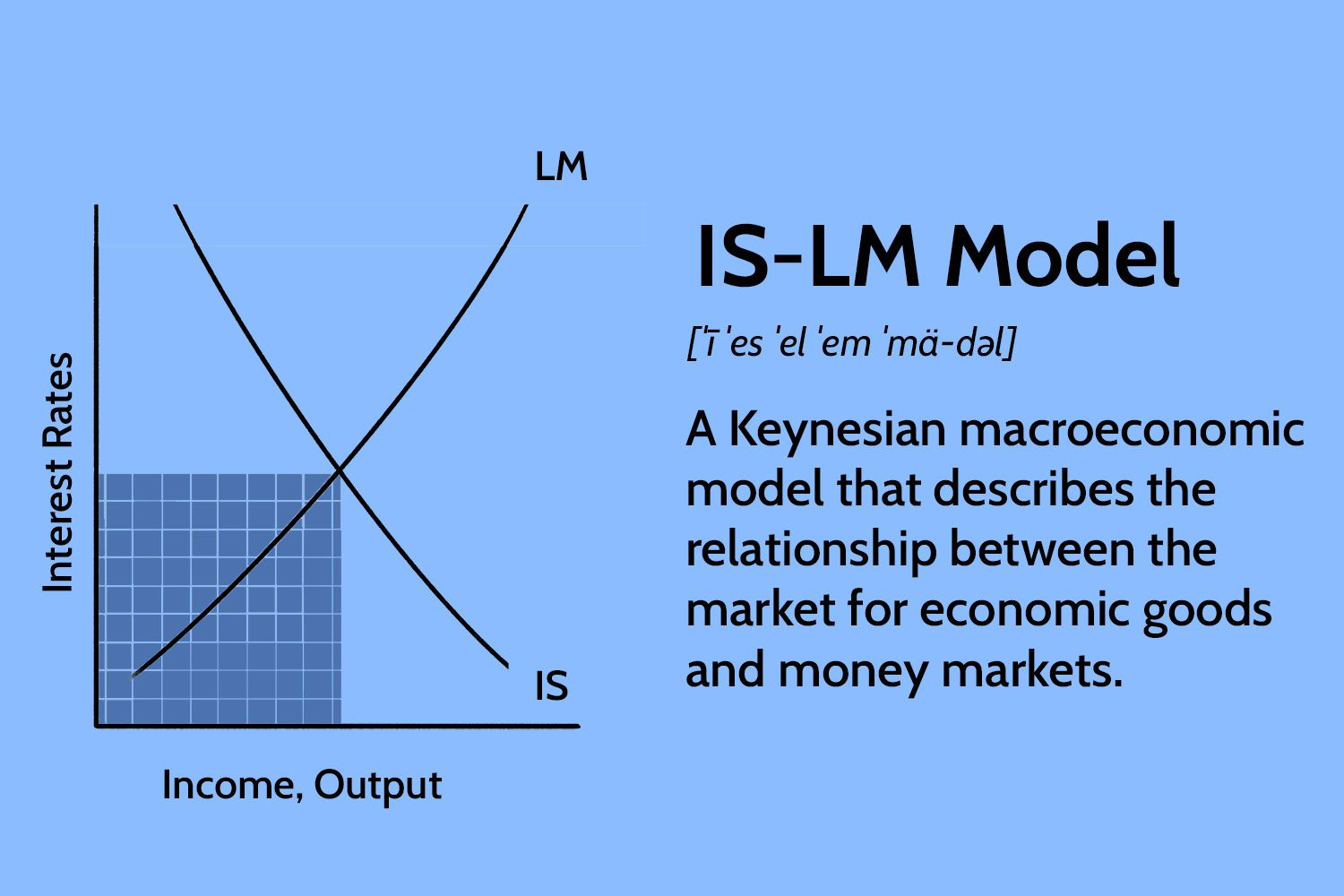
1. IS-LM model
The IS-LM model shows the relationship between the goods market and the money market in an economy. The IS curve represents equilibrium in the goods market, plotting the combination of interest rates and national income where investment equals savings. The LM curve represents equilibrium in the money market, plotting the interest rate and income combination where money demand equals the fixed money supply. The intersection of the IS and LM curves determines the equilibrium interest rate and national income in the economy given fiscal and monetary policies.
2. Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the use of government taxation and spending to influence economic conditions. Fiscal policy impacts interest rates and aggregate output, represented by shifts in the IS curve in the IS-LM model.
+ Expansionary fiscal policy involves increased government spending and/or reduced taxes to boost aggregate demand during recessions.
+ Contractionary fiscal policy does the opposite - cutting spending and/or raising taxes to cool demand and restrain inflation.
3. Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to central bank actions to influence money supply and interest rates. Monetary policy impacts interest rates and aggregate output through shifts in the LM curve in the IS-LM model.
+ Expansionary monetary policy aims to lower interest rates and increase money supply to boost lending, investment, and consumer spending during economic slowdowns.
+ Contractionary monetary policy does the opposite - raising interest rates and reducing money supply growth to dampen inflationary pressures.
4. Business cycle
The business cycle describes how economies go through regular ups and downs in economic activity.
+ During expansions, the economy is growing as production and employment rise. Expansions lead to a peak where the economy is operating at full capacity.
+ After the peak, contractions or recessions occur - economic activity declines, firms make less, unemployment goes up.
+ At the bottom is the trough, after which a new expansion begins and the cycle repeats. Governments use policies to try to flatten the sharp rises and falls over the business cycle.
5. Money Supply
Money supply refers to the total amount of money circulating in an economy at a given time. It includes currency in circulation and the money held in checking accounts and savings accounts. Central banks control money supply growth by using monetary policy tools like reserve requirements, interest rates, and open market operations.
6. Balance of Payments
The balance of payments tracks all money flowing in and out of a country from international trade and investment. If more money is going out than coming in, there is a deficit. If more money is coming in than going out, there is a surplus. It impacts currency values and economic growth.
7. Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign direct investment (FDI) occurs when an individual or company from one country makes a long-term investment in a business or physical assets in another country. Inward FDI can boost economic growth and development in the recipient country through capital financing, knowledge transfers, and job creation. Outward FDI allows domestic firms to expand globally.
D/ DETAILED OUTLINE
I. Section 1: Events Overview
A. Introduction:
● 2-3 first sentences: Start with an introduction that briefly explains the purpose of this section
Hints: To provide an overview of recent economic events and their significance.
B. & C.Event/Condition 1/2/3(if applicable)
● 1-2 first sentences - Identification and Nature: Clearly identify and describe the first event or condition that has taken place in the Vietnamese economy in the past 12 months. Emphasize its macroeconomic nature.
Example: Ukraine - Russia war
- The escalating conflict between Russia and Ukraine that erupted into full-scale war in February 2022 has had pronounced macroeconomic ripples globally, including in distant Vietnam
● 2-3 next sentences - Direct Sectoral Impact: Discuss which sector(s) have been directly impacted by this event. Explain how the event may have affected these sectors in the short run and the long run.
Example: Ukraine - Russia war
- Disruptions to food and energy exports from the Black Sea region, leading to global shortages and price spikes (29% drop in Ukraine's grain production in 2022/202)
- Weighs on global growth and trade, dampening demand for Vietnamese exports (The combined trade of Vietnam with Russia and Ukraine stood at 7.6 billion U.S. dollars in 2021, accounting for 1.2 percent of Vietnam's total import-export turnover, according to data from the Vietnamese Ministry of Industry and Trade).
Charge your account to get a detailed instruction for the assignment