Management & Change
INNOVATION MANAGEMENT - A3
Reflective Essay
Table of Contents
expand_more expand_less
Table of Contents
DETAILED INSTRUCTION
- The essay, comprising 1000 words, should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, using the first-person narrative to reflect on how the course influenced your understanding of innovation management
- Required to introspectively analyze and discuss your learning experiences, focusing on their impact on your personal and professional development.
- Adherence to formatting guidelines, the D.I.E.P. framework, and academic integrity is crucial, with an emphasis on the essay's authenticity and relevance to your career and personal growth.
Suggested structure:
1/ Introduction (suggested 100 words)
2/ Body (suggested 700-800 words, divided into 2-3 paragraphs)
● Paragraph 1 (suggested 250 words) – Quality Encounter of Learning
● Paragraph 2 (suggested 300 words) – Deep Insights
● Paragraph 3 (suggested Optional, 200 words) – Significance and Impac
● Career Implications (suggested 150 words)
3/ Conclusion (suggested 150 words)
1. Innovation Management: The process of managing ideas and inventions effectively to commercialize them. It involves organizing, directing, and controlling resources to bring about the successful adoption of new products and processes.
2. Creativity: The ability to generate novel and useful ideas. It's the starting point for innovation, involving imagination and the formation of new connections between existing ideas.
3. Entrepreneurship: The act of creating a business or businesses while building and scaling it to generate a profit, often characterized by innovation and risk-taking.
4. Innovation: The practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services.
5. Sustainability: The ability to maintain or improve systems and processes in a way that ensures long-term ecological balance, often a key consideration in modern innovation management.
6. Wealth Creation: The process of creating economic value, or more assets and income, often an outcome of successful innovation and entrepreneurship.
7. Organizational Models of Innovation: Frameworks and structures used by businesses to manage and support innovation processes.
8. Problem-Solving: The process of finding solutions to complex or difficult issues, central to the creative front end of innovation.
9. Team Dynamics: The behavioral relationships between members of a team, which can significantly influence the innovation process.
10. Entrepreneurial Behavior: Actions and mindsets that are characteristic of entrepreneurs, such as risk-taking, proactiveness, and innovativeness.
11. Business Growth: The process of improving some measure of a company's success, which can be achieved through innovation.
12. Collaborative Work: Working together effectively as a team, crucial for the innovation process, especially in the ideation and implementation stages.
13. Innovative Organization Traits: Characteristics that are commonly found in organizations that are successful in innovation, like adaptability, creativity, and a culture of continuous improvement.
14. Commercialization: The process of bringing new products or services to market, a key aspect of innovation management.
15. Ideation: The creative process of generating, developing, and communicating new ideas, an essential part of the innovation process.
16. Sustaining innovation
Sammarize:
Module: Factors affecting creativity in individuals and teams
● Creativity refers to ‘the production of novel and useful ideas in any domain’ (Amabile et al. 1996, p. 1155)
● Factors that facilitate creativity in employees The Componential Theory of Individual Creativity (Amabile 1997)
○ Expertise: Memory for factual knowledge, technical proficiency and special talents in a specific domain
○ Creative thinking skills: The ability to take on new perspectives on a given problem
○ Intrinsic task motivation: Motivation driven by deep interest and involvement in the work, by curiosity and/or a personal sense of challenge
○ Be curious – Curiosity may have killed the cat but for creatives it is a lifeline to idea generation
○ Unleash your imagination – Develop the ability to create vivid images in your mind not immediately present to the senses or never before perceived in reality
○ Develop ‘lateral thinking’ – Use indirect and creative approaches to solve a problem by viewing the problem in a new and unusual light
○ Be willing to ‘unlearn’ – Be willing to go beyond learned assumptions
○ Take risks – Don’t be afraid to take risks with new ideas/news ways of thinking
● The role of positive emotions in individual creativity
○ Emotions are affective responses to what happens in the environment
○ Emotions can be positive (e.g., happiness, love, interest) or negative (e.g., anger, sadness, anxiety) depending on how a person evaluates stimuli
→ Broaden & Build Theory (Fredrickson 2001) – Positive emotions broadens peoples thoughts/action repertoire and builds lasting personal resources
Module: Creativity in organizations
● Factors that promote creativity in organizations (Amabile 1997)
○ Organizational encouragement – the existence of an organizational culture that encourages and promotes creativity
○ Supervisory encouragement – a supervisor who acts as a good role model, supports the team and shows confidence in the team
○ Work group support – a diversely skilled team that supports each other, communicates effectively and is open to new ideas
○ Sufficient resources – access to appropriate resources (funds, materials, facilities etc)
○ Challenging work – a sense of having to work hard on challenging tasks and important projects
○ Freedom – freedom to decide on what work to do or how to do it
● Factors that impede creativity in organizations
○ Organizational impediments – the existence of an organizational culture that impedes creativity by creating internal conflict and political problems, harsh criticism of new ideas etc
○ Workload pressure – extreme time pressure and unrealistic workload expectations etc
● Big C, Little c and Mini c
○ ‘Big C’ (eminent) creativity: relatively rare displays of creativity that have a major impact on others
○ ‘Little c’ (everyday) creativity: daily problem solving and the ability to adapt to change
○ ‘Mini c’ (intrapersonal) creativity: the novel and personally meaningful interpretation of experiences, actions, and events
Module: How innovation present in firm and in marketplace
● The degree of innovation present in firms
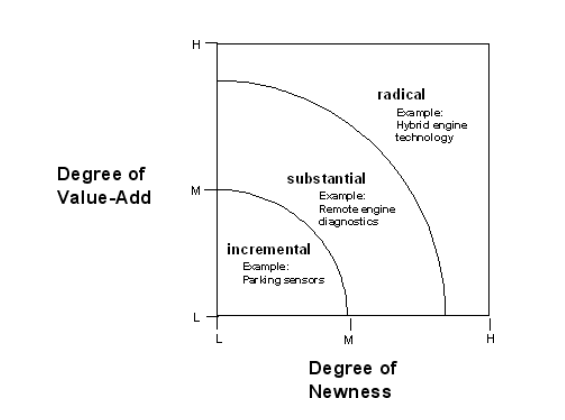
● Incremental innovations: A series of small improvements or upgrades made to a company's existing products, services, processes or methods. The changes implemented through incremental innovation are usually focused on improving an existing product's development efficiency, productivity and competitive differentiation.
● Substantial innovation is one that provides a substantial degree of added value and/or newness to a company. It’s an innovation that has the potential to create brand new business opportunities for the company (and perhaps even for other companies, e.g., advertising), grants the company a new competitive advantage and perhaps even places that company as one of the leaders in its field (if it wasn’t already).
● Radical Innovation
○ Radical innovation, concerned with the exploration of new technology, is fundamentally different from incremental innovation that is concerned with exploitation of existing technology.
○ Radical innovation is a product, process, or service with either unprecedented performance features or familiar features that offer potential for significant improvements in performance and cost.
○ It creates such a dramatic change in processes, products, or services that they can potentially transform existing markets or industries, or create new ones. (Leifer, Mcdermott, O'Connor, Peters, Rice, & Veryzer,2000)
● Impact of firm’s innovation on the marketplace
● 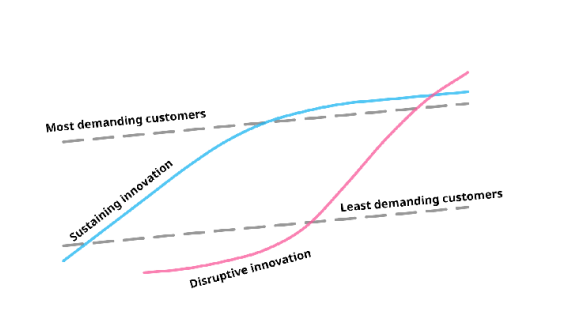
● Sustaining innovation
○ Refers to the type of innovations that exist in the current market and improves and grows the existing market.
○ For example, nearly all modern cars can be considered to be sustaining innovations. If we look at for example Toyota Prius (first launched in 1997), the basic functionalities of the car have stayed pretty much the same. It only continues getting slightly better with every iteration, continuing to cater the needs of a typical Prius customer.
○ SI is how established companies move along established improvement trajectories – improvements along dimensions historically valued by customers.
● Disruptive Innovation – Clayton M Christensen
○ A disruptive innovation is an innovation that creates a new market and value network and eventually disrupts an existing market and value network, displacing established market leading firms, products and alliances.
○ It describes a process by which a product or service takes root initially in simple applications at the bottom of a market and then relentlessly moves up market, eventually displacing established competitors.
Module: INNOVATION PROCESSES: 3 Types
Three Innovation Models (Govindarajan & Trimble, 2013)
1) Model S is for Small Improvements / Initiatives
2) Model R is for Repeatable Innovations
3) Model C is for Custom Innovations
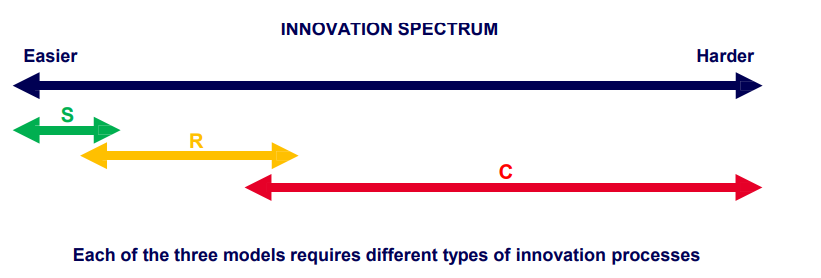
1) Model S is for Small improvements (Govindarajan & Trimble, 2013)
● A culture that supports innovation is helpful here (not much so for the other 2 models)
● Every employee can and should innovate when they spot an opportunity
● Small projects
● Also known as Continuous Improvement or Kaizen (made famous by Toyota), Six Sigma, quality programs, etc.
● Typically applicable to Process Innovation, but also product/Service innovation
● Key to success is employee motivation
Charge your account to get a detailed instruction for the assignment