People & Organisation
INNOVATION MANAGEMENT - A3 (Template Version)
Creativity in organizations Factors that promote creativity in organizations (Amabile 1997) Organizational encouragement – the existence of an organizational culture that encourages and promotes creativity Freedom – freedom to decide on what work to do or how to do it
Table of Contents
expand_more expand_lessTable of Contents
DETAILED INSTRUCTION
The essay, comprising 1000 words, should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, using the first-person narrative to reflect on how the course influenced your understanding of innovation management
Required to introspectively analyze and discuss your learning experiences, focusing on their impact on your personal and professional development.
Adherence to formatting guidelines, the D.I.E.P. framework, and academic integrity is crucial, with an emphasis on the essay's authenticity and relevance to your career and personal growth.
Suggested structure:
1/ Introduction (suggested 100 words)
2/ Body (suggested 700-800 words, divided into 2-3 paragraphs)
- Paragraph 1 (suggested 250 words) – Quality Encounter of Learning
- Paragraph 2 (suggested 300 words) – Deep Insights
- Paragraph 3 (suggested Optional, 200 words) – Significance and Impact
- Career Implications (suggested 150 words)
3/ Conclusion (suggested 150 words)
- Innovation Management: The process of managing ideas and inventions effectively to commercialize them. It involves organizing, directing, and controlling resources to bring about the successful adoption of new products and processes.
- Team Dynamics: The behavioral relationships between members of a team, which can significantly influence the innovation process.
- Entrepreneurial Behavior: Actions and mindsets that are characteristic of entrepreneurs, such as risk-taking, proactiveness, and innovativeness.
- Business Growth: The process of improving some measure of a company's success, which can be achieved through innovation.
Module: Factors affecting creativity in individuals and teams
- Creativity refers to ‘the production of novel and useful ideas in any domain’ (Amabile et al. 1996, p. 1155)
- Factors that facilitate creativity in employees The Componential Theory of Individual Creativity (Amabile 1997)
-
- Expertise: Memory for factual knowledge, technical proficiency and special talents in a specific domain
- Creative thinking skills: The ability to take on new perspectives on a given problem
- Be willing to ‘unlearn’ – Be willing to go beyond learned assumptions
- Take risks – Don’t be afraid to take risks with new ideas/news ways of thinking
- The role of positive emotions in individual creativity
-
- Emotions are affective responses to what happens in the environment
Module: Creativity in organizations
- Factors that promote creativity in organizations (Amabile 1997)
-
- Organizational encouragement – the existence of an organizational culture that encourages and promotes creativity
- Freedom – freedom to decide on what work to do or how to do it
- Factors that impede creativity in organizations
-
- Organizational impediments – the existence of an organizational culture that impedes creativity by creating internal conflict and political problems, harsh criticism of new ideas etc
- Workload pressure – extreme time pressure and unrealistic workload expectations etc
- Big C, Little c and Mini c
-
- ‘Big C’ (eminent) creativity: relatively rare displays of creativity that have a major impact on others
- ‘Little c’ (everyday) creativity: daily problem solving and the ability to adapt to change
- ‘Mini c’ (intrapersonal) creativity: the novel and personally meaningful interpretation of experiences, actions, and events
Module: How innovation present in firm and in marketplace
- The degree of innovation present in firms
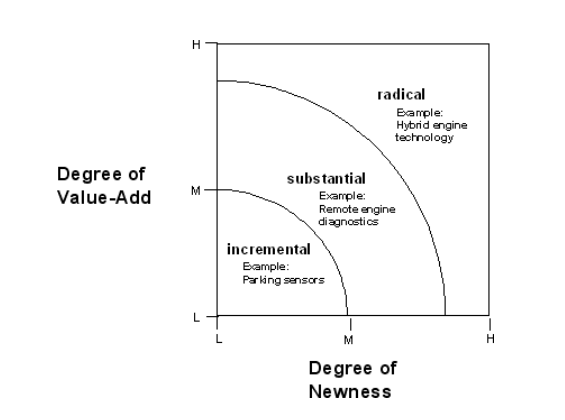
- Incremental innovations: A series of small improvements or upgrades made to a company's existing products, services, processes or methods. The changes implemented through incremental innovation are usually focused on improving an existing product's development efficiency, productivity and competitive differentiation.
- Radical Innovation
-
- Radical innovation, concerned with the exploration of new technology, is fundamentally different from incremental innovation that is concerned with exploitation of existing technology.
Charge your account to get a detailed instruction for the assignment